Home > Respiratory Physiotherapy
Respiratory Physiotherapy
What is Respiratory Physiotherapy?
Physiotherapy techniques are provided to individuals coping with an array of medical respiratory conditions. The overarching goals of these interventions are the management of breathlessness and symptom alleviation, mobility and function improvement or maintenance, and airway clearance and cough enhancement or support.1
The term “airway clearance techniques” (ACTs) refers to a wide array of strategies employed to eliminate excessive secretions from the respiratory system. These specialised techniques are designed to assist individuals in effectively clearing mucus and secretions from their lungs. The overall objective is to improve overall lung function, enhance oxygenation, and reduce the risk of respiratory infections. Additionally, ACTs can promote the re-expansion of collapsed lung areas, thus improving gas exchange and mitigating inflammatory responses within the respiratory system.2

PEP Mechanisms
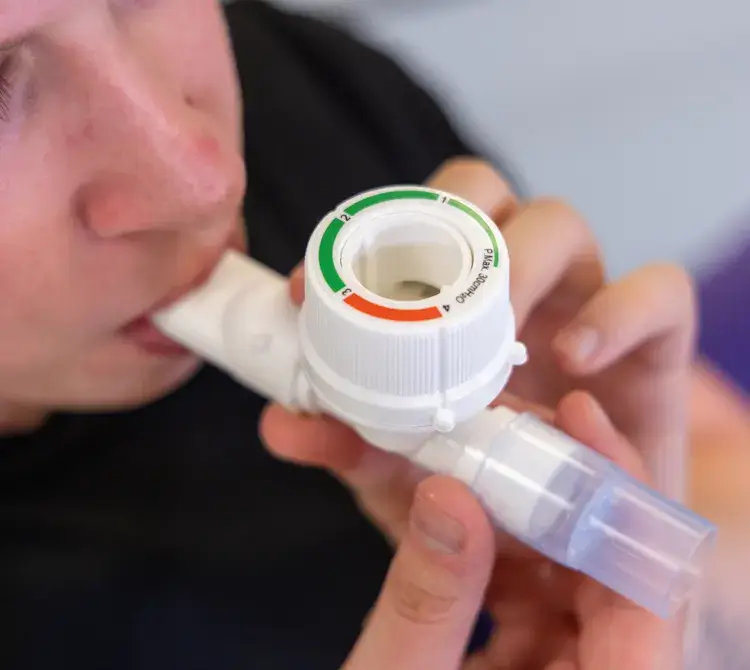
Positive Expiratory Pressure Therapy (PEP) are an airway clearance technique that is designed to address the needs of patients with acute or chronic respiratory failure, neurological or musculoskeletal impairments, chronic pulmonary disorders, or reduced lung capacities.
This therapeutic approach introduces resistance into the exhalation process, thereby augmenting the effort required during expiration.
PEP devices generate controlled vibrations upon the patient’s exhalation, which in turn facilitate the mobilisation of mucus sticking to the airway surfaces. Following a series of exhalations through the device, the individual naturally stimulates a cough reflex to effectually clear the mucus from their airways.3
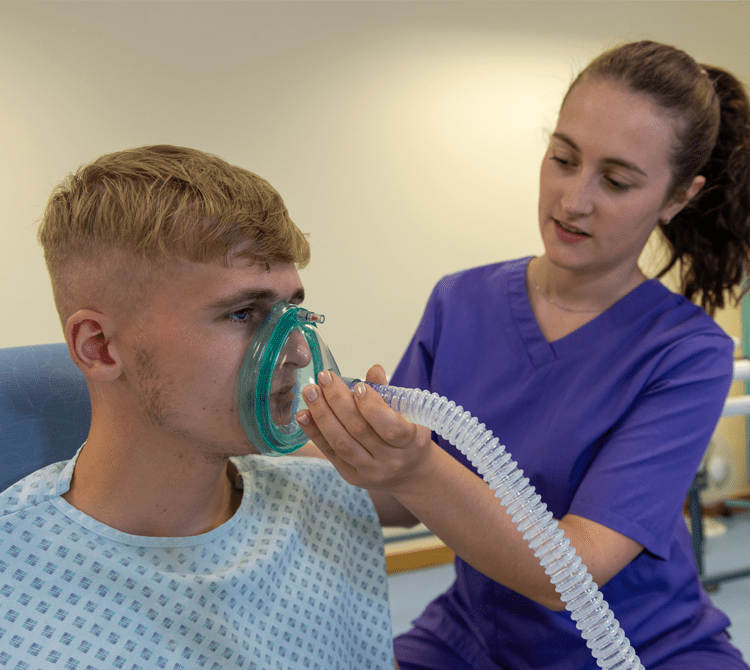

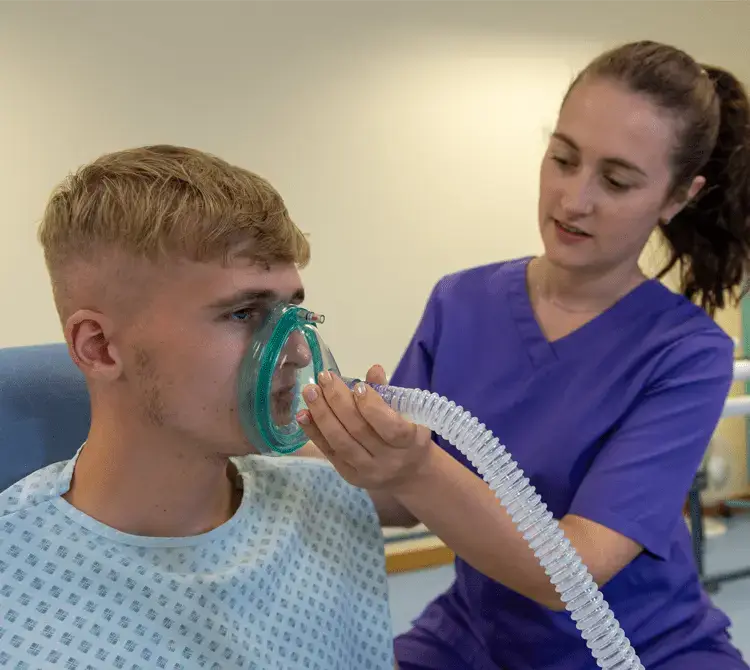
Manual insufflation-exsufflation also known as Cough Assist
Cough Assist therapy aids in secretion clearance by employing a two-step process: it initially applies positive pressure to expand the lungs, quickly transitioning to a negative pressure phase to produce a high expiratory flow rate, thereby simulating a natural cough reflex.
This therapeutic approach can be administered through various means, including a mask, mouthpiece, endotracheal, or tracheostomy tube.
This change in pressure helps to dislodge mucus adhering to the airway walls and facilitates movement out of the lungs.
Manual Insufflation-Exsufflation (MIE), proves particularly beneficial for patients with weakened cough reflexes or a reduced ability to clear secretions independently.2
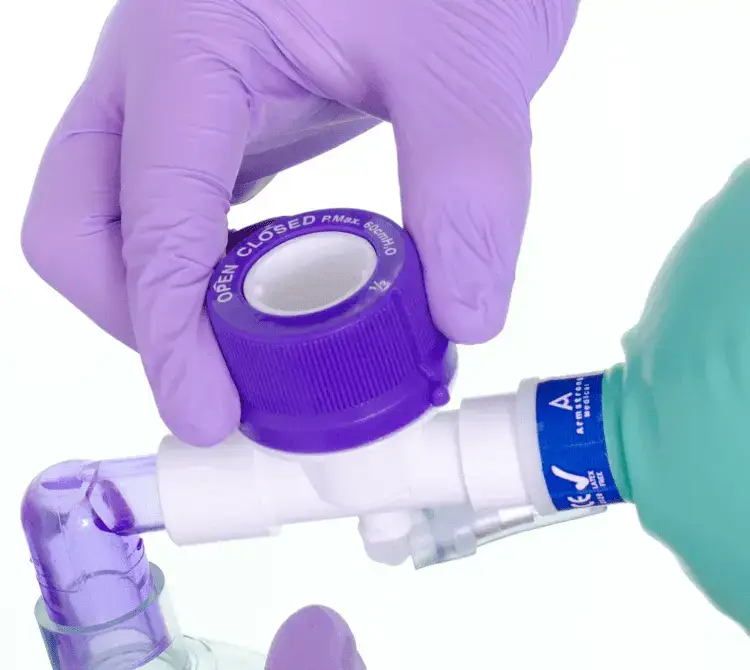
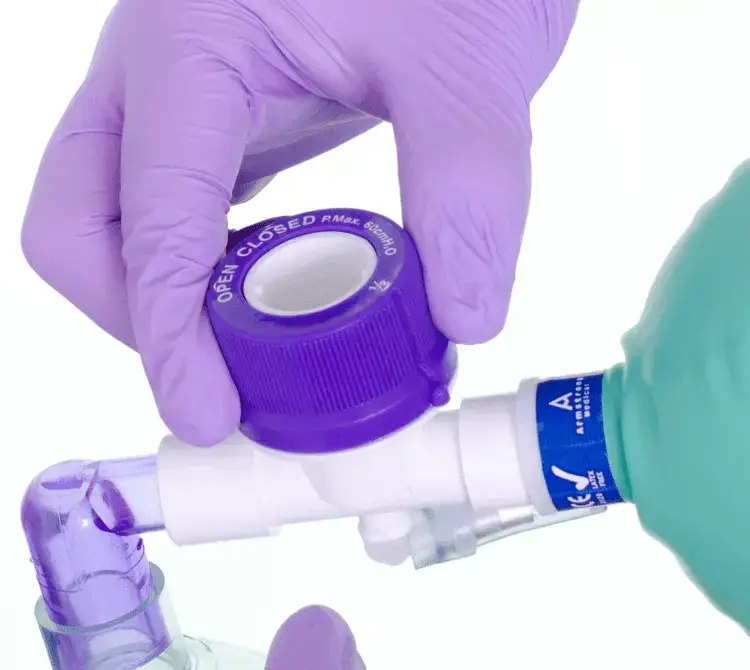
Manual Hyperinflation (MHI)
Manual hyperinflation involves the use of a Mapleson-C bagging circuit to encourage alveolar recruitment and proximal movement of airway secretions. This is achieved by delivery of a high-volume inspiration, inspiratory hold, and quick release expiration.
It is a respiratory therapy technique used in the management of ventilated patients or patients self-ventilating through a tracheostomy to increase lung volumes and aid secretion clearance when used in conjunction with suctioning4
Frequently Asked Questions
It is most useful in patients with an ineffective cough due to muscle weakness, in conditions such as muscular dystrophies, myasthenia gravis, MND etc. It may also be used for the respiratory ICU patient as secretion encumbrance is one of the main reasons for respiratory failure after extubation. Mechanical insufflation-exsufflation (MI-E) can be efficient to manage copious secretions and help to avoid reintubation.
Using these two therapies in combination can prevent and treat complications of inadequate secretion clearance and impaired respiratory function.
Humidified high flow with AquaNASE® maintains mucociliary function and improves oxygenation by delivering flows close to the patients’ peak inspiratory requirement, the humidification element can assist with mucociliary clearance and Ultra-PEP can be used to mobilise secretions, assist with airway clearance, and prevent or reverse post-operative atelectasis.
Physiotherapy Products
Products that help physiotherapists provide tailored support to patients requiring respiratory support.
- Bott, J, et al. “Guidelines for the Physiotherapy Management of the Adult, Medical, Spontaneously Breathing Patient.” Thorax, vol. 64, no. Suppl 1, 30 Apr. 2009, pp. i1–i52,.
- Belli, Stefano, et al. “Airway Clearance Techniques: The Right Choice for the Right Patient.” Frontiers in Medicine, vol. 8, no. 1, 2021, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7902008/, https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2021.544826.
- Franks, Lisa J, et al. “Comparing the Performance Characteristics of Different Positive Expiratory Pressure Devices.” Respiratory Care, vol. 64, no. 4, 22 Jan. 2019, pp. 434–444, https://doi.org/10.4187/respcare.06410.
- Paulus, Frederique, et al. “Benefits and Risks of Manual Hyperinflation in Intubated and Mechanically Ventilated Intensive Care Unit Patients: A Systematic Review.” Critical Care, vol. 16, no. 4, 2012, p. R145, https://doi.org/10.1186/cc11457.
Get in touch
We are committed to protecting and preserving the privacy of our visitors when visiting our site or communicating electronically with us.